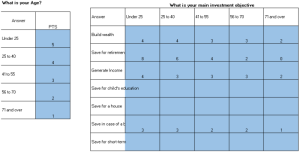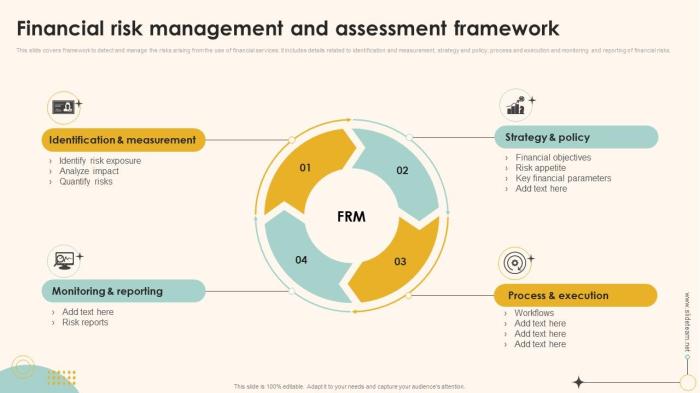
As Financial risk assessment takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers with casual formal language style into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
Financial risk assessment plays a crucial role in decision-making processes by identifying, analyzing, and managing potential risks that could impact an organization’s financial stability and success. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the key components of financial risk assessment, explore various risk assessment methods, discuss effective risk management strategies, and shed light on the concepts of risk tolerance and risk appetite.
Introduction to Financial Risk Assessment

Financial risk assessment is a crucial process that helps organizations identify, evaluate, and prioritize potential risks that could impact their financial stability and performance. By conducting a thorough risk assessment, businesses can make informed decisions and implement strategies to mitigate or manage these risks effectively.
Types of Risks in Financial Risk Assessment
There are several types of risks involved in financial risk assessment, including:
- Market Risk: The risk of financial loss due to changes in market conditions such as interest rates, exchange rates, and commodity prices.
- Credit Risk: The risk of loss arising from a borrower’s inability to repay a loan or meet their financial obligations.
- Operational Risk: The risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, systems, or external events.
- Liquidity Risk: The risk of not being able to meet short-term financial obligations due to a lack of liquid assets.
Key Components of Financial Risk Assessment Process
The key components of a financial risk assessment process include:
- Identification of Risks: This involves identifying and categorizing potential risks that could affect the organization’s financial health.
- Risk Analysis: Assessing the likelihood of occurrence and potential impact of each identified risk on the organization.
- Risk Evaluation: Prioritizing risks based on their significance and developing strategies to manage or mitigate them.
- Monitoring and Review: Continuously monitoring the effectiveness of risk management strategies and reviewing the risk assessment process regularly.
Risk Assessment Methods
Financial risk assessment involves various methods to analyze and evaluate potential risks that may impact an organization’s financial stability. Quantitative and qualitative methods are commonly used to assess financial risks, each providing unique insights into the risk exposure of a business.
Quantitative Methods
Quantitative methods in financial risk assessment involve the use of mathematical models and statistical tools to measure and quantify risks. These methods rely on historical data, probability theory, and complex calculations to assess the likelihood of various risk scenarios. Some common quantitative methods include:
- Scenario Analysis: Scenario analysis involves creating different scenarios based on potential market conditions or events to assess the impact on the organization’s financial performance. By analyzing multiple scenarios, organizations can better understand the range of possible outcomes and prepare accordingly.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Sensitivity analysis helps organizations identify how changes in certain variables or factors can affect their financial position. By analyzing the sensitivity of key variables, businesses can evaluate the potential impact of fluctuations in market conditions and make informed decisions to mitigate risks.
- Stress Testing: Stress testing involves subjecting the organization’s financial model to extreme scenarios or stressors to evaluate its resilience and ability to withstand adverse conditions. By simulating severe market shocks or economic downturns, businesses can assess their risk exposure and develop strategies to manage potential crises.
Qualitative Methods
Qualitative methods focus on subjective assessments and expert judgment to evaluate financial risks that may not be easily quantifiable. These methods involve qualitative analysis, risk mapping, and expert opinions to identify and assess potential risks. Some qualitative methods include:
- Expert Opinion: Expert opinion involves consulting industry experts, analysts, or experienced professionals to gather insights on potential risks and their possible impact on the organization. Expert opinions can provide valuable qualitative assessments that complement quantitative analysis.
- Risk Mapping: Risk mapping involves visualizing and categorizing different types of risks based on their likelihood and impact on the organization. By mapping out risks, businesses can prioritize and address key risk areas effectively.
Risk Management Strategies
Risk management plays a crucial role in mitigating financial risks for organizations. By identifying, assessing, and addressing potential risks, companies can protect their assets and financial stability. Risk management frameworks provide a structured approach to navigating uncertainties in the business environment, helping organizations make informed decisions and minimize negative impacts.
Risk Diversification
Diversification is a common risk management strategy that involves spreading investments across different assets to reduce exposure to any single risk. By diversifying their portfolio, organizations can lower the overall risk level and avoid significant losses in case one asset underperforms.
Hedging
Hedging is another effective risk management strategy that involves using financial instruments to offset potential losses. For example, a company may use futures contracts to lock in the price of a commodity, protecting against price fluctuations in the future. By hedging, organizations can minimize the impact of market volatility on their financial performance.
Insurance
Insurance is a traditional risk management strategy that helps transfer the financial risk to an insurance company in exchange for a premium. Whether it’s property insurance, liability insurance, or business interruption insurance, having the right insurance coverage can protect organizations from unexpected events that could lead to financial losses.
Contingency Planning
Contingency planning involves developing strategies to respond to potential risks and uncertainties. By anticipating various scenarios and having a plan in place, organizations can minimize the impact of unforeseen events on their financial health. Contingency planning helps companies stay prepared and resilient in the face of challenges.
Risk Tolerance and Risk Appetite

Risk tolerance and risk appetite are crucial concepts in financial risk assessment. Risk tolerance refers to the level of risk that an organization or individual is willing to accept in pursuit of their financial goals. On the other hand, risk appetite is the amount of risk that an entity is prepared to take on to achieve its objectives, considering factors such as capital, liquidity, and regulatory requirements.
Impact of Risk Tolerance Levels on Decision-Making Processes
In the context of financial risk assessment, the risk tolerance levels of an organization can significantly influence decision-making processes. A higher risk tolerance may lead to more aggressive investment strategies, potentially yielding higher returns but also exposing the organization to greater risk. Conversely, a lower risk tolerance may result in more conservative approaches, limiting potential gains but also reducing the likelihood of significant losses.
It is essential for organizations to carefully assess their risk tolerance levels to ensure alignment with their overall financial objectives.
Strategies for Aligning Risk Tolerance with Organizational Goals
- Conduct a thorough risk assessment: Organizations should evaluate their risk exposure across various areas, such as market, credit, and operational risks, to determine their overall risk tolerance.
- Establish clear risk management policies: Developing robust risk management policies and procedures can help ensure that risk tolerance levels are effectively communicated and implemented throughout the organization.
- Regularly review and adjust risk tolerance levels: As market conditions and organizational goals evolve, it is essential to periodically reassess and potentially adjust risk tolerance levels to maintain alignment with strategic objectives.
In conclusion, mastering the art of financial risk assessment is essential for organizations looking to thrive in today’s dynamic business environment. By understanding the risks involved, implementing robust risk assessment methods, and adopting effective risk management strategies, companies can safeguard their financial well-being and make informed decisions that align with their goals and objectives. Stay informed, stay proactive, and stay ahead of financial uncertainties with a solid foundation in financial risk assessment.
FAQ
What is the importance of financial risk assessment?
Financial risk assessment is crucial as it helps organizations identify potential risks, evaluate their impact, and implement strategies to mitigate these risks, ensuring financial stability and success.
How do risk tolerance and risk appetite differ in financial risk assessment?
Risk tolerance refers to the level of risk an organization is willing to accept, while risk appetite defines the amount of risk it is willing to take to achieve its objectives. Understanding and aligning these concepts are vital in decision-making processes.
What are some common risk management strategies for specific types of financial risks?
Common risk management strategies include diversification, hedging, insurance, and contingency planning, tailored to address different types of financial risks such as market risk, credit risk, and operational risk.