Beginning with Risk tolerance and risk appetite, this topic delves into how these factors shape decision-making processes within businesses, offering a unique perspective that is both informative and engaging.
Exploring the nuances of risk tolerance and risk appetite, this discussion sheds light on their impact on strategic choices and overall business performance.
Risk Tolerance and Risk Appetite
Risk tolerance and risk appetite are two crucial concepts in the field of risk management for businesses. Understanding the differences between these terms and how they impact decision-making is essential for effective risk management strategies.
Definition of Risk Tolerance and Risk Appetite
Risk tolerance refers to the level of risk that an organization or individual is willing to accept in pursuit of their objectives. It is a measure of how much uncertainty or potential loss they can handle without compromising their goals.
Risk appetite, on the other hand, is the amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to take in order to achieve its strategic objectives. It reflects a company’s willingness to engage in risk-taking activities to meet its goals.
Differences between Risk Tolerance and Risk Appetite
- Risk tolerance is more focused on the individual or organization’s ability to withstand risk, while risk appetite is about the willingness to actively seek out and take on risk.
- Risk tolerance is often quantified in terms of specific metrics or thresholds, while risk appetite is more qualitative and strategic in nature.
- Risk tolerance is a more defensive approach to risk management, whereas risk appetite is a more proactive stance towards risk.
Impact on Decision-Making in Businesses
Both risk tolerance and risk appetite play a significant role in shaping decision-making processes within businesses. Understanding these concepts helps organizations make informed choices when it comes to evaluating opportunities, setting objectives, and managing potential risks.
By aligning risk tolerance and risk appetite with business objectives, companies can create a risk management framework that allows for effective decision-making, resource allocation, and strategic planning.
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is a crucial process that involves identifying, analyzing, and evaluating potential risks that could impact an organization’s objectives. By conducting risk assessments, businesses can better understand their risk exposure and develop strategies to mitigate or manage these risks effectively.
Tools and Methods Used in Risk Assessment
Risk assessment can be carried out using various tools and methods, including:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Scenario analysis
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- Monte Carlo simulation
Importance of Regular Risk Assessments for Businesses
Regular risk assessments are essential for businesses due to the following reasons:
- Identifying potential risks early on allows businesses to implement proactive measures to mitigate these risks before they escalate.
- Regular risk assessments help in ensuring compliance with regulations and standards, reducing the likelihood of fines or legal issues.
- By evaluating risks regularly, businesses can make informed decisions and allocate resources effectively to address high-priority risks.
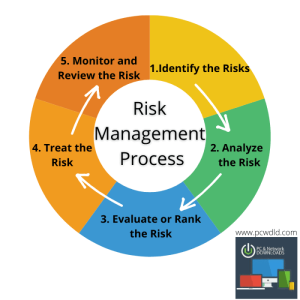
Risk Management

Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks followed by coordinated and economical application of resources to minimize, monitor, and control the probability and impact of unfortunate events or to maximize the realization of opportunities. It involves analyzing potential risks and developing strategies to address them effectively.
Proactive vs. Reactive Risk Management Strategies
Proactive risk management involves identifying and addressing risks before they occur, focusing on prevention rather than reaction. This approach allows organizations to be prepared and implement measures to mitigate potential risks in advance. On the other hand, reactive risk management involves responding to risks after they have occurred, dealing with the consequences rather than preventing them. While reactive measures are necessary in some situations, proactive strategies are generally more effective in minimizing the impact of risks.
- Proactive risk management helps organizations anticipate and prevent potential risks, leading to better preparedness and resilience.
- Reactive risk management is essential for responding to unexpected events and minimizing the damage caused.
- Combining proactive and reactive strategies can create a comprehensive risk management approach that addresses risks at all stages.
Best Practices for Effective Risk Management in Organizations
Effective risk management in organizations involves a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and responding to risks to achieve business objectives and protect assets. Here are some best practices to enhance risk management:
- Establish a clear risk management policy and framework to guide decision-making and actions.
- Regularly assess and prioritize risks based on their impact and likelihood of occurrence.
- Implement risk mitigation strategies and controls to reduce the probability and impact of identified risks.
- Communicate and engage stakeholders in the risk management process to ensure alignment and transparency.
- Monitor and review the effectiveness of risk management measures and adjust them as needed to address changing circumstances.
Risk Tolerance

Risk tolerance refers to the level of risk that an individual is willing to accept in their investment or decision-making process. Several factors can influence an individual’s risk tolerance, including their financial goals, age, investment experience, and personal circumstances.
Factors Influencing Risk Tolerance
- Financial Goals: Individuals with long-term financial goals may have a higher risk tolerance as they have more time to recover from any potential losses.
- Age: Younger individuals may have a higher risk tolerance as they have more time to ride out market fluctuations.
- Investment Experience: Those with more experience in investing may be more comfortable with taking on higher levels of risk.
- Personal Circumstances: Factors such as income stability, family responsibilities, and overall financial situation can also impact an individual’s risk tolerance.
Variation of Risk Tolerance Across Industries
- High-Risk Industries: Industries such as technology startups and biotech companies are known for their high-risk nature, attracting investors with higher risk tolerance.
- Low-Risk Industries: On the other hand, industries like utilities and consumer staples are considered low-risk, appealing to investors with lower risk tolerance.
- Regulatory Environment: Some industries, like finance and healthcare, may have stricter regulations that influence risk tolerance among investors.
Strategies for Improving Risk Tolerance
- Diversification: Spreading investments across different asset classes can help reduce overall risk exposure.
- Education: Increasing financial literacy and understanding investment options can boost confidence in managing risks.
- Gradual Approach: Gradually increasing exposure to riskier investments can help individuals become more comfortable with higher levels of risk.
- Professional Advice: Consulting with financial advisors can provide guidance on managing risk and building a suitable investment portfolio.
Risk Appetite
Risk appetite refers to the level of risk that an organization is willing to take in pursuit of its objectives. It is a crucial component of risk management as it helps in setting boundaries and guiding decision-making processes. By clearly defining risk appetite, organizations can ensure that they are taking on risks that are aligned with their strategic goals and objectives.
Significance of Risk Appetite in Risk Management
- Provides a clear understanding of the types and levels of risks that an organization is willing to accept.
- Helps in aligning risk-taking activities with the overall strategy of the organization.
- Assists in establishing risk tolerance levels and risk management frameworks.
- Aids in prioritizing risks and allocating resources effectively.
Alignment with Organization’s Goals
- By determining risk appetite, organizations can ensure that their risk-taking activities support the achievement of their strategic objectives.
- It helps in avoiding unnecessary risks that may hinder the organization’s progress towards its goals.
- Allows management to make informed decisions about which risks to accept, mitigate, or avoid based on their impact on the organization’s goals.
Communication and Implementation of Risk Appetite
- Developing a risk appetite statement that clearly articulates the organization’s approach to risk-taking.
- Regularly communicating the risk appetite statement to employees at all levels of the organization.
- Integrating risk appetite into strategic planning, decision-making processes, and performance evaluation.
- Implementing risk appetite through the establishment of risk limits, monitoring mechanisms, and reporting procedures.
In conclusion, understanding risk tolerance and risk appetite is essential for businesses to navigate uncertainties effectively and make informed decisions that align with their objectives.
Top FAQs
What is the difference between risk tolerance and risk appetite?
Risk tolerance refers to the level of risk an individual or organization is willing to accept, while risk appetite defines the amount of risk they are willing to take to achieve their objectives.
How do risk tolerance and risk appetite influence decision-making in businesses?
Both risk tolerance and risk appetite play crucial roles in shaping strategic decisions by guiding how much risk a business is willing to undertake to meet its goals.
What are some common factors that influence an individual’s risk tolerance?
Factors such as age, financial situation, past experiences, and personal risk preferences can impact an individual’s risk tolerance.